Hyperthyroidism
The condition where the thyroid gland produces hormones more than normal is called Hyperthyroidism. In hyperthyroidism, T3 and T4 levels increase while TSH levels decrease. It is about 10 times more common in women than men.
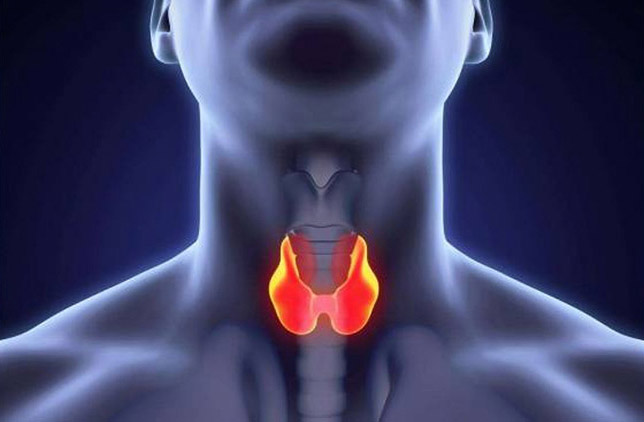
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
- Graves' disease: The most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disease. It occurs more frequently in women. Antibodies produced by the body's immune system stimulate the thyroid gland, causing it to work more than normal.
- Hyperfunctional nodular goiter: Hyperthyroidism occurs as a result of thyroid nodules producing excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. These nodules are called "toxic" (hot) nodules. If there is only one nodule, it is called a toxic adenoma, and if there are multiple nodules, it is called toxic multinodular goiter.
- Thyroiditis: An autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland. It is more common in women. Due to chronic inflammation in the thyroid gland, thyroid hormones stored in the follicular cells of the thyroid are released into the bloodstream, causing elevated thyroid hormone levels.
What are the Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism?
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism are as follows:
- Irritability
- Heat intolerance
- Weight loss
- Palpitations
- High blood pressure
- Protrusion of the eyes
- Sensitivity to light and double vision
Hyperthyroidism Treatment in Antalya
Hyperthyroidism treatment is performed with appropriate methods, including medication, radioactive iodine, surgery, percutaneous thyroid ablation, and thyroid artery embolization treatments.
Interventional Radiology Specialist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bülent Çekiç has conducted examinations and can provide you with hyperthyroidism treatment in Antalya Muratpaşa. Feel free to contact us for more information.
The methods used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism can be explained as follows:
Medication Treatment:
Medications that reduce thyroid hormone synthesis are used (anti-thyroid drugs). Patients using these medications may develop agranulocytosis (decrease in white blood cells), which increases the risk of infections. Additionally, 20% of patients experience skin rashes, allergic reactions, and joint pains.
Radioactive Iodine Treatment
RAI (Radioactive Iodine) is administered orally in the form of Iodine (I-131) molecules. These radioactive iodine molecules enter the thyroid cells and destroy them. Its effect begins to show after 6-18 weeks. After treatment, due to radiation exposure, the patient must stay away from children and pregnant women for 5-7 days.
The most significant side effect of radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment is the permanent development of hypothyroidism due to the destruction of the thyroid gland by the radioactive iodine molecules. Therefore, the patient will require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
Surgical Treatment
In surgical treatment, the entire thyroid gland is removed. However, there are complications such as nerve damage and damage to the parathyroid glands, which control calcium metabolism. Additionally, after surgery, the removal of the entire thyroid gland leads to permanent hypothyroidism, and the patient will need lifelong thyroid hormone therapy.
Percutaneous Thyroid Ablation and Thyroid Artery Embolization Treatments
In simple (diffuse) goiter and multinodular goiter, the efficacy of thyroid artery embolization treatment is high. In this method, a needle is inserted through the femoral artery from the groin area, and embolizing substances (similar to sand particles) are used to block three or four feeding arteries of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland shrinks to normal size within 1-2 months without losing its function. In patients with Graves' disease, the dose of anti-thyroid medications can decrease by up to 80%.
In cases of hyperfunctional nodular goiter, if there is only one or two hot nodules, percutaneous thermal ablation (Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation) treatment methods may be used. In this method, a needle is inserted through the skin on the neck to enter the thyroid nodule, where it is destroyed using heat. After the ablation process, the thyroid nodule loses its viability, and within three months, it shrinks by 80%.
In some patients, both treatment methods can be applied together (thyroid artery embolization and percutaneous thyroid ablation). This is generally related to the number of nodules and the size of the thyroid gland.
Advantages of Percutaneous Thyroid Ablation and Thyroid Artery Embolization
- The procedure is done under local anesthesia. The patient is discharged on the same day.
- No incision marks on the neck.
- The patient does not lose the thyroid gland, hypothyroidism does not develop, and lifelong thyroid hormone therapy is not needed.
- Within 3 months, the thyroid nodule/thyroid gland shrinks by 80%.

 TR
TR