Thyroid nodules are a health concern that often progresses without symptoms and can cause anxiety when discovered. Fortunately, modern medicine offers patients reassuring solutions with non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment methods. In this article, you will find scientific and guiding information about all the details and advantages of non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment by Interventional Radiology Specialist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bülent Çekiç.
| Question | Answer |
| Treatment duration? | Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment usually takes 30-60 minutes. |
| Is there pain? | Thanks to local anesthesia, most patients don't feel pain during the procedure. |
| Is it safe? | It's a safe method when performed by experienced physicians. |
| Is it permanent? | Treated nodules show 80-95% permanent reduction. |
| Cosmetic advantage? | Non-surgical methods provide nodule treatment without leaving neck scars. |
| Alternative to surgery? | Yes, non-surgical treatment methods provide solutions without requiring surgery. |
| Success rate? | Success rate is generally high, with 80-95% success reported. |
| Recovery time after procedure? | Patients can usually return to normal activities the same day. |
What is a thyroid nodule?
A thyroid nodule refers to an abnormal growth or mass on the butterfly-shaped thyroid gland located in the lower neck area, which is responsible for producing hormones that regulate body metabolism. These nodules are common in adults and most are benign. While most people don't show symptoms due to thyroid nodules, thyroid nodule symptoms typically include visible neck swelling, difficulty swallowing, or voice changes.
Thyroid nodule detection is usually done through physical examination, and additional tests such as ultrasound and thyroid biopsy (fine needle aspiration biopsy) may be needed to determine the nature of the nodule and appropriate treatment method. Thyroid hormone testing is also frequently used. Understanding the characteristics of thyroid nodules is crucial for effective management of potential risks.
What is non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
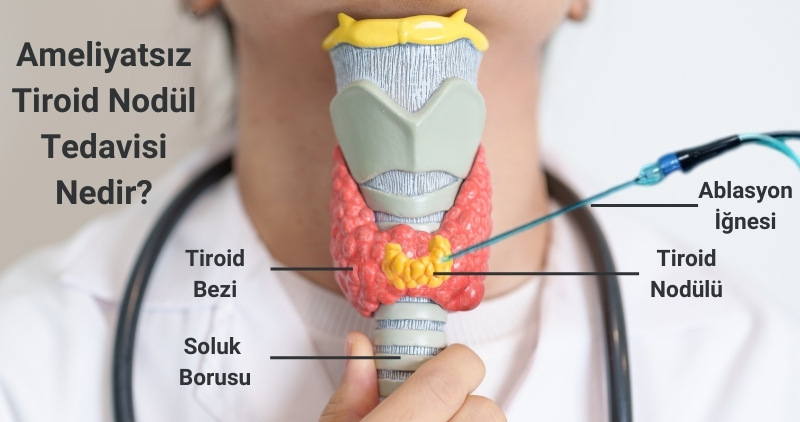
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment includes techniques such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), and ethanol injection, which work by directly applying heat or alcohol to the tissue to shrink nodules. These methods are precise and minimally invasive as they are performed under ultrasound guidance. They are particularly effective in benign cases, reducing nodule size and symptoms without requiring surgical intervention. Clinical studies show that these methods have high success rates with minimal complications and offer a safe alternative to traditional thyroid surgery, which is a popular approach.
What is percutaneous ablation?
Percutaneous ablation involves placing a needle-like probe through the skin to directly apply destructive energy to the tumor. It's typically preferred for patients who cannot undergo thyroid surgery due to tumor location, size, or general health condition. Techniques like radiofrequency and microwave ablation use heat, while cryoablation uses freezing temperatures. Studies indicate that percutaneous ablation shows high effectiveness in treating small primary or metastatic tumors, particularly in the liver and lungs, with fewer side effects. According to a study published in Radiology journal in 2023, microwave ablation reported a 90% success rate in local tumor control for small liver tumors.
Percutaneous ablation is also an effective method that can be used in non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment. Especially in fluid-filled, viscous cystic thyroid nodules, this method involves inserting a needle into the nodule under ultrasound guidance to apply radiofrequency, microwave, or alcohol. This procedure helps shrink the nodule and alleviate symptoms. A study published in 2008 showed that single-session ethanol ablation is a safe and effective treatment method for viscous cystic thyroid nodules. After 6 months, a 93.6% reduction in nodule volume was observed, and no serious complications were reported during this period.
How is non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment performed?
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment is typically performed using minimally invasive techniques such as radiofrequency ablation, microwave ablation, or ethanol ablation. During RFA, a thin needle is placed into the thyroid nodule under ultrasound guidance. The needle emits thermal energy that destroys the nodule tissue and allows it to shrink over time. In ethanol ablation, a small amount of alcohol is injected into the nodule to cause cell death and nodule shrinkage. Both procedures are performed under local anesthesia, offering quick recovery and minimal discomfort. These methods are ideal for patients with benign nodules who don't want thyroid nodule surgery and effectively reduce nodule size and symptoms.
What precautions should be taken after non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
- Avoid heavy lifting and exercise: Physical strain can increase pressure in the neck and treatment area, potentially causing bleeding or disrupting the healing process.
- Monitor swelling and pain: Mild discomfort is normal, but severe swelling or pain may indicate complications like infection or hematoma requiring immediate medical attention.
- Drink plenty of water: Adequate fluid intake supports healing and helps eliminate cellular debris from the treated area.
- Avoid NSAIDs and aspirin: These blood-thinning medications can increase bleeding risk by preventing blood clotting; paracetamol is safer for pain management.
- Limit neck movement: Excessive movement can cause irritation in the treated area, delaying healing.
- Avoid hot contact: Hot baths or hot water bottles can increase blood flow to the treatment area, raising the risk of bleeding or swelling.
- Don't massage or apply pressure: This can disrupt tissue regeneration and lead to infection spread.
- Apply cold compresses correctly: Apply cold intermittently during the first 24 hours to reduce swelling, but avoid direct skin contact.
- Follow a soft diet: If recommended, a soft diet reduces neck muscle tension and minimizes discomfort during swallowing.
- Rest voice if necessary: If nodules are close to vocal cords, they may cause hoarseness or voice strain; limit speaking to allow healing.
- Monitor infection signs: Redness, warmth, fever, or pus at the treatment site may indicate infection; prompt treatment is needed to prevent complications.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Both can impair immune function, delaying tissue repair and increasing complication risk.
- Wear loose clothing: Tight collars or scarves that pressure the neck can be uncomfortable and hinder healing.
- Don't miss follow-up appointments: Regular ultrasound checks are important for monitoring nodule size and early detection of possible regrowth or complications.
- Report breathing difficulty immediately: Though rare, airway obstruction can occur; it requires immediate medical attention.
- Follow medication instructions: If antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, use them completely to reduce infection risk and manage inflammation.
What are non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment methods?
For patients seeking alternatives to surgical intervention, various non-surgical methods are available for thyroid nodule treatment. These techniques cause less discomfort and provide faster recovery compared to traditional surgery due to their minimally invasive nature. Here are some of the most common non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment methods:
Microwave ablation
Works similarly to RFA, but uses microwaves to generate heat and destroy the nodule.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
Shrinks and destroys thyroid nodules using heat generated by radio waves.
Ethanol ablation
Involves injecting alcohol into the nodule to cause cell death and nodule shrinkage.
Laser ablation
Uses laser energy to generate heat and destroy nodule tissue.
High-intensity focused ultrasound
Uses focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the nodule without cutting.
When is non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment performed?
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment is performed in specific cases. It's ideal for patients with benign nodules causing swallowing difficulties, neck discomfort, or cosmetic concerns who wish to avoid surgery. It's also suitable for patients who cannot undergo surgery due to medical conditions or those with small, limited nodules. These methods are also preferred as alternatives to surgical intervention in patients who have previously undergone surgery and have recurring nodules.
Are there cases where non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment is not appropriate?
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment may not be suitable in certain cases, particularly when the nodule is malignant (cancerous) or when ultrasound and thyroid nodule biopsy findings indicate a risk of thyroid cancer. In such cases, surgical intervention is necessary for complete removal of the nodule and proper pathological examination.
Additionally, nodules larger than 4 cm may not respond well to non-surgical treatments, as nodules of this size can cause complications by pressing on surrounding tissues. These treatments may be risky in conditions such as hyperthyroidism or bleeding disorders. If there is an active infection in the neck area, it must be treated before beginning treatment. In such complex cases, it's important for patients to be comprehensively evaluated by an endocrinologist and surgeon.
What are the advantages of non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
| Advantage | Description |
| Minimally invasive | Less tissue damage and scarring |
| Quick recovery | Shorter recovery time compared to surgery |
| Local anesthesia | Eliminates risks associated with general anesthesia |
| Outpatient procedure | Performed without requiring hospitalization |
| Low complication risk | Reduced risk of infection and bleeding |
| Preservation of thyroid function | Less impact on overall thyroid activity |
| Cosmetic advantage | No visible neck scarring |
| Targeted treatment | Precise treatment with minimal effect on surrounding tissues |
Non-surgical treatment methods such as radiofrequency ablation and ethanol ablation offer significant advantages in managing thyroid nodules. Being minimally invasive, they reduce tissue damage and scarring as they can be performed through small holes. These procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia, avoiding the risks of general anesthesia. They can mostly be performed as outpatient procedures, allowing patients to return home the same day.
The recovery process is generally shorter, requiring fewer restrictions on daily activities. These methods precisely target nodules while preserving surrounding healthy thyroid tissue and maintaining overall thyroid function. This is particularly beneficial for patients who want to avoid lifelong thyroid hormone therapy often necessary after more comprehensive surgical procedures. The cosmetic advantages are also noteworthy; there is no visible scarring, making it an attractive option for those concerned about appearance.
Studies have shown high success rates in reducing nodule size and alleviating symptoms such as pressure or cosmetic issues. Additionally, the risks of complications such as infection and bleeding are significantly lower compared to traditional surgery. This targeted and effective treatment approach offers a highly personalized and patient-friendly solution for treating benign thyroid nodules.
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment costs
For non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment costs, you can schedule a preliminary examination appointment with Interventional Radiology Specialist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bülent Çekiç, who provides services in cities such as Antalya Muratpaşa center, Istanbul, and Ankara. To evaluate your suitability for treatment, thyroid biopsy and necessary tests must first be performed based on criteria such as the patient's nodule structure and size. After these evaluations, a personalized treatment plan and pricing are determined according to the patient's condition and needs. Please call us to get detailed information about non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment cost and make an appointment.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is there pain during non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
No, non-surgical thyroid nodule treatments such as radiofrequency ablation, microwave ablation, and ethanol ablation are generally painless due to the use of local anesthesia.
Most patients only feel mild pressure or warmth during the procedure. Studies show that these treatments are generally well-tolerated and cause less discomfort compared to surgical options. There may be mild discomfort, tenderness, or swelling after the procedure, but these conditions can usually be easily controlled with over-the-counter pain relievers, cold compresses, and keeping the head elevated, allowing for faster recovery.
How long does non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment take?
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatments typically take 30 to 60 minutes.
Duration may vary depending on the size, number, and location of nodules. Treatment time may be longer in complex cases involving large or multiple nodules. However, small and easily accessible nodules can be treated in less time. The use of advanced imaging techniques and intervention by an experienced specialist can also shorten the procedure time. Generally, there's no need to worry; these treatments are safe, and most patients can return to normal activities within a few days.
What is the success rate of non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
Non-surgical thyroid nodule treatments, such as radiofrequency ablation and ethanol ablation, generally have a high success rate. Studies show that in most patients, there is an 80-95% reduction in nodule size and relief of symptoms.
Factors that increase success include small nodule size, benign pathology, and accurate targeting of the nodule. Larger nodules, those in complex locations near critical structures, or nodules with malignant features may reduce the success rate. Experienced specialists and advanced imaging techniques can enhance treatment effectiveness and reduce the risk of complications. Overall, these treatments are considered effective and safe in the management of benign thyroid nodules.
Is hospitalization required after non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
No, hospitalization is generally not required after non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment, as these procedures are minimally invasive.
These treatments are typically outpatient procedures, and patients can go home the same day. Since local anesthesia is used, the risks associated with general anesthesia are avoided, and the recovery process is faster. Small puncture sites heal quickly, and most patients can return to normal activities within a few days. Therefore, hospitalization is generally not necessary unless complications arise.
Will there be scars after non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment?
No, typically there will be no or only minimal scarring after non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment.
This is because these procedures create small holes using only tiny needles or probes, rather than large surgical incisions. Minimal tissue damage leads to faster healing and less scar tissue formation. Since local anesthesia is used, there is no need for large incisions or stitches. Additionally, advanced imaging techniques allow for precise treatment without damaging surrounding tissues. As a result, the risk of visible scarring is significantly lower compared to traditional surgery.
What should people with thyroid nodules be careful about?
Patients with thyroid nodules should have regular check-ups, as nodules can change in size or characteristics over time. Symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, neck discomfort, or changes in voice should be monitored. Regular ultrasound examinations and hormone tests are recommended to evaluate nodule activity and overall thyroid function. It is also advisable to avoid iodine-rich foods or supplements unless recommended by a doctor, and to maintain a healthy diet.
Do thyroid nodules go away on their own?
Most thyroid nodules do not go away on their own. Benign nodules typically remain stable or grow slowly. In some cases, small benign nodules may shrink, but malignant nodules require medical intervention. Regular follow-up and appropriate treatment are essential for managing risks.
What should people with thyroid nodules avoid eating?
People with thyroid nodules should avoid excessive iodine intake, as it may promote nodule growth or disrupt thyroid function. Foods such as seaweed, kelp, and certain iodine supplements should be limited. It is also helpful to avoid large amounts of soy products and cruciferous vegetables like cabbage and broccoli, as they can interfere with thyroid hormone production.
For more detailed information about non-surgical thyroid nodule treatment in Ankara and to schedule an examination, you can contact Interventional Radiology Specialist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Bülent Çekiç. You can also read our article on Thyroid Artery Embolization.
This article is for informational and consultation purposes. The recommendations of your surgeon, who will examine you and perform your surgery, should take precedence.

 TR
TR